Code for KDE
Code for KDE
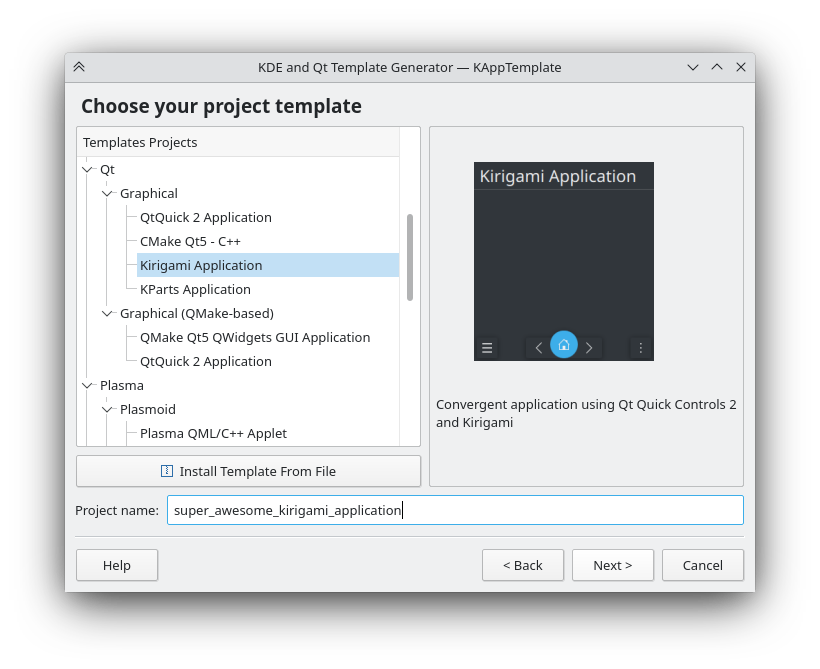
Summary: KDE uses C++ programming language with the Qt Toolkit and KDE Frameworks. Coders with every level of experience are welcome. We have coding mentorship. Linux is the recommended operating system to program for KDE. We use kde-builder as a development environment.
Programming languages for KDE development |
|---|
To develop KDE applications, you’ll need familiarity with:
Prior programming experience is helpful but not required. |
Mentorship Programs for New Developers |
|---|
| KDE offers mentorship opportunities for beginners through established open source programs:
We also provide a curated list of learning resources to help you improve your programming skills. |
Recommended operating systems |
|---|
For best results, use a Linux-based system when developing KDE software. Supported distributions include:
You may also develop on Windows, macOS, or FreeBSD. However:
|
Setting up your KDE Development environment |
|---|
| Use kde-builder to configure your KDE development environment and build KDE software.
Collaborate with other developers—KDE development is team-based. Follow the official setup guide to get started. |
Programming tools for KDE developers |
|---|
|
How to start contributing your programming skills to KDE |
|---|
Steps:
GitlabIn KDE Gitlab(invent.kde.org), coding tasks are organized by project. 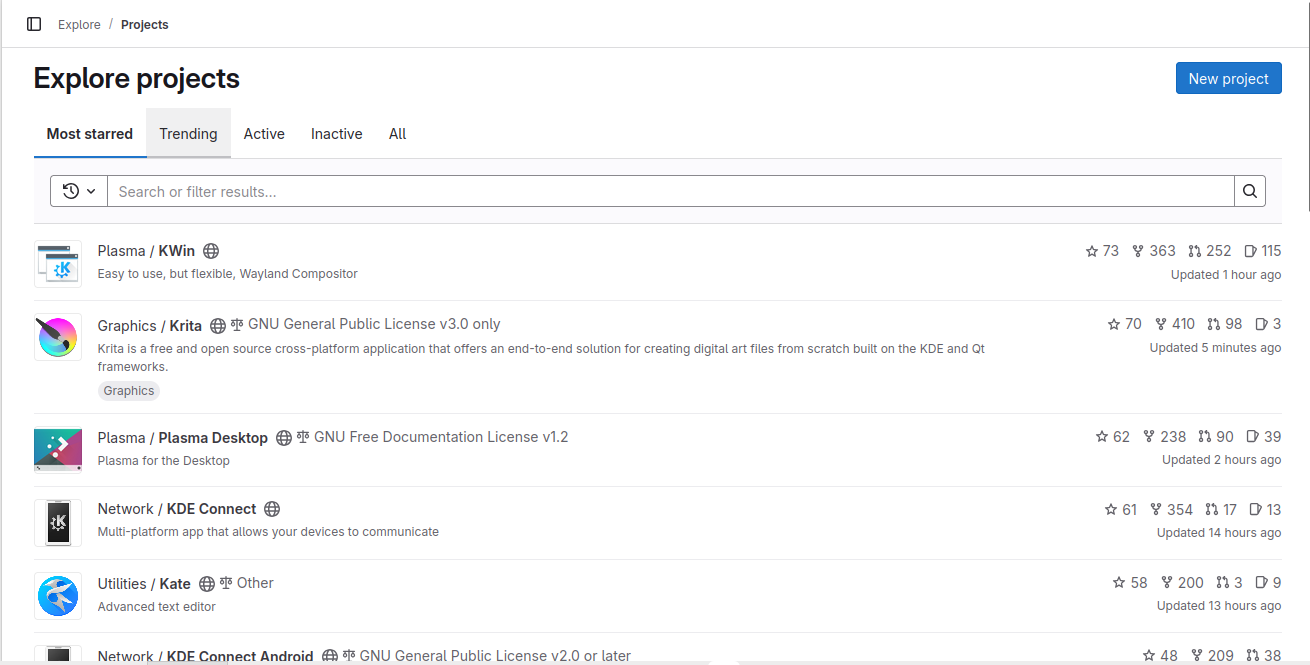 Click on the sidebar icon and select issues.  Click on an issue, familiarize yourself with it. 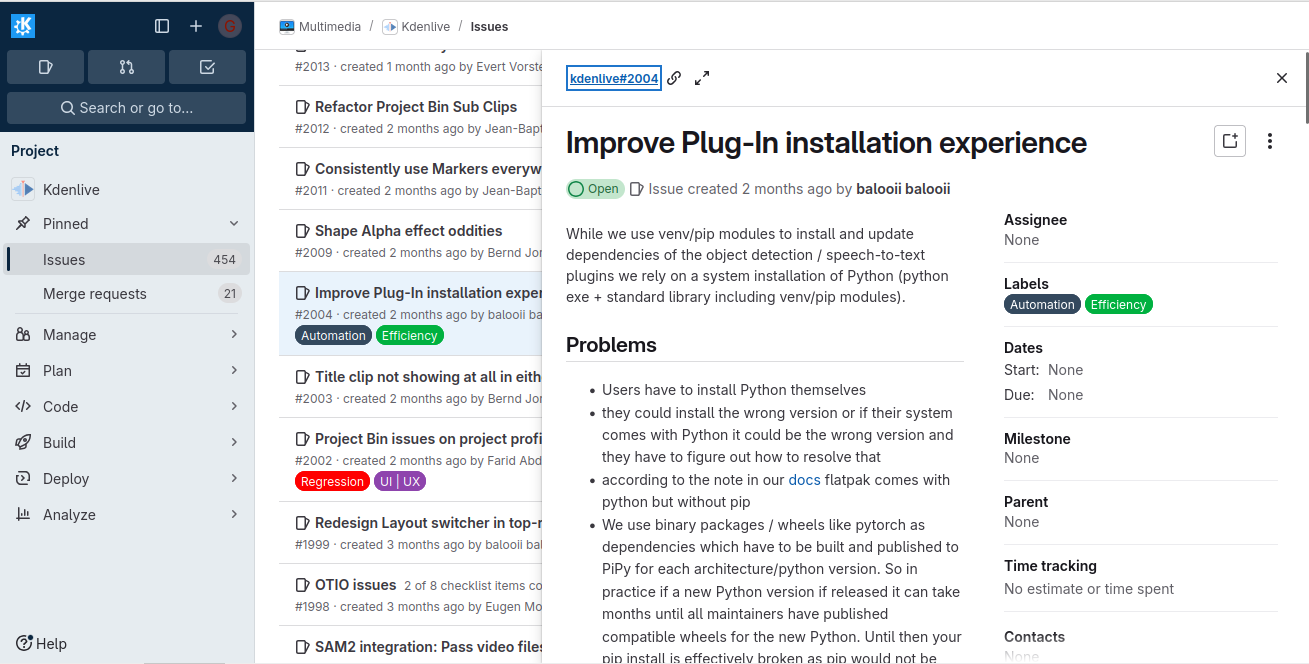 Contribute if you’re confident that you can solve an issue. Read the Readme file and Contribute file. 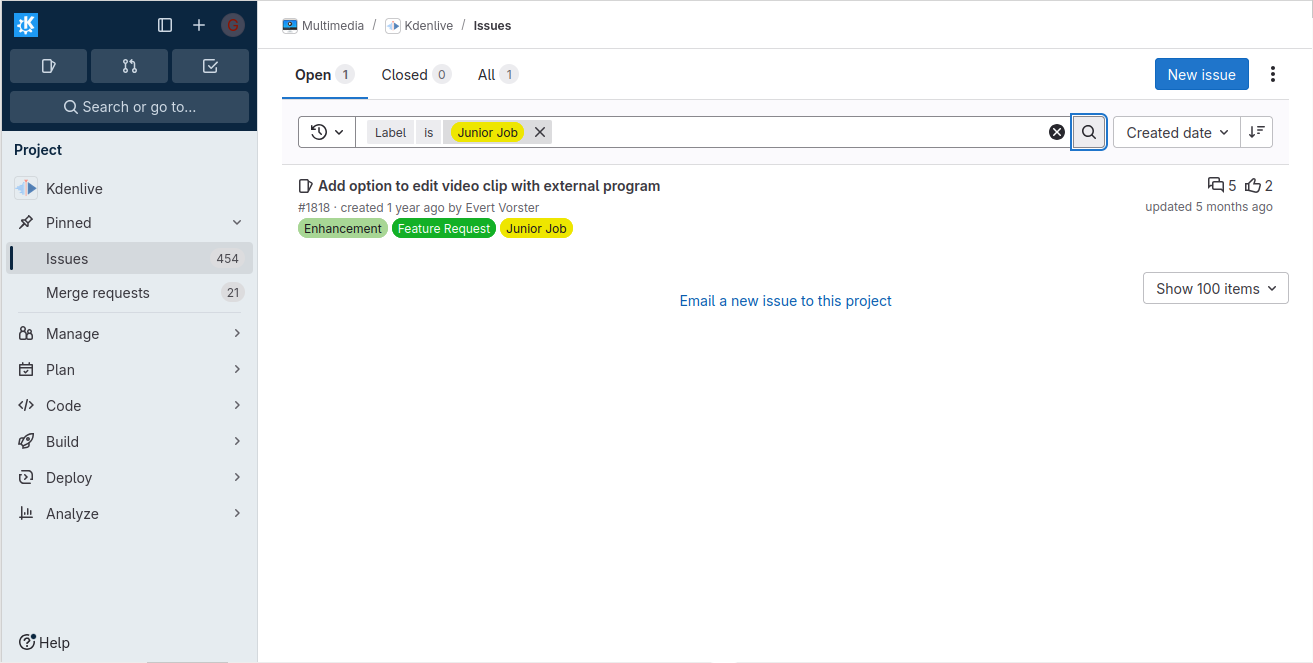 If you’re a beginner, follow the above steps. Then, in the top search bar, enter “Label,”(remember to press Enter after each) “is,” “Junior Job” or “Beginner Friendly.” You’ll get a list of Beginner tasks. PhabricatorLog in with your identity.kde.org. 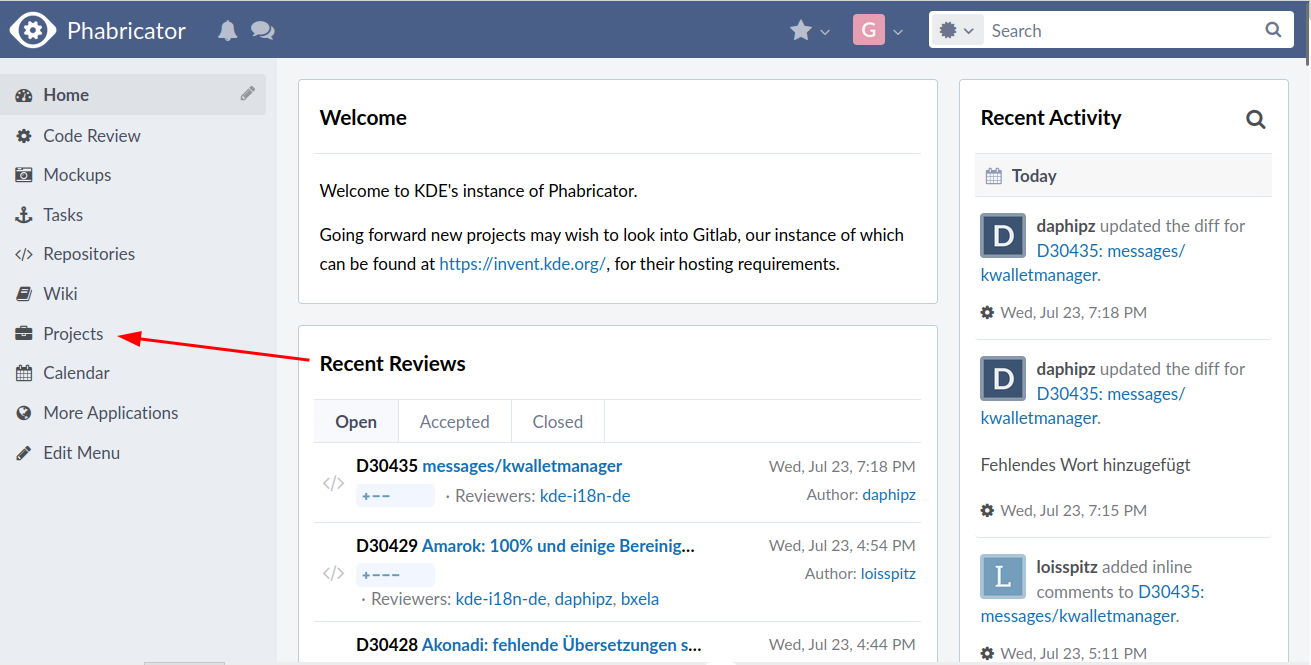 Choose Projects on the Left Sidebar. 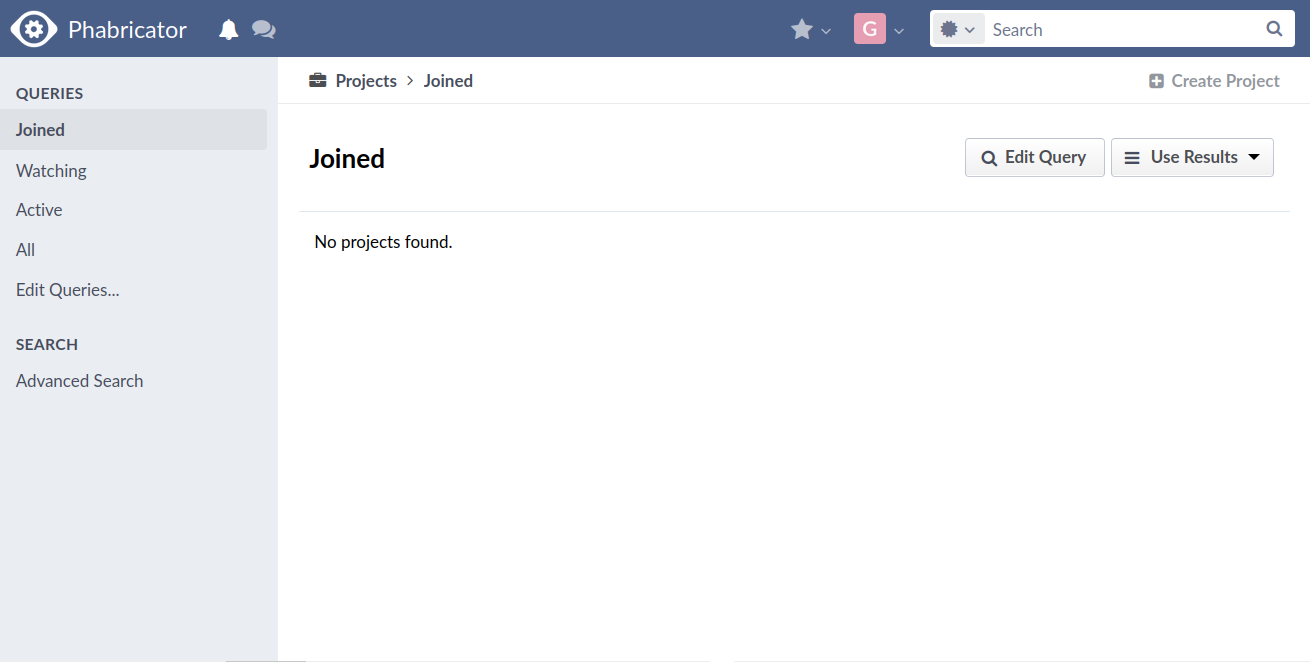 If you get a “No projects found.” result, click on the “Edit Query” button in the Upper Right corner.  From the “Members” form field, remove your name. 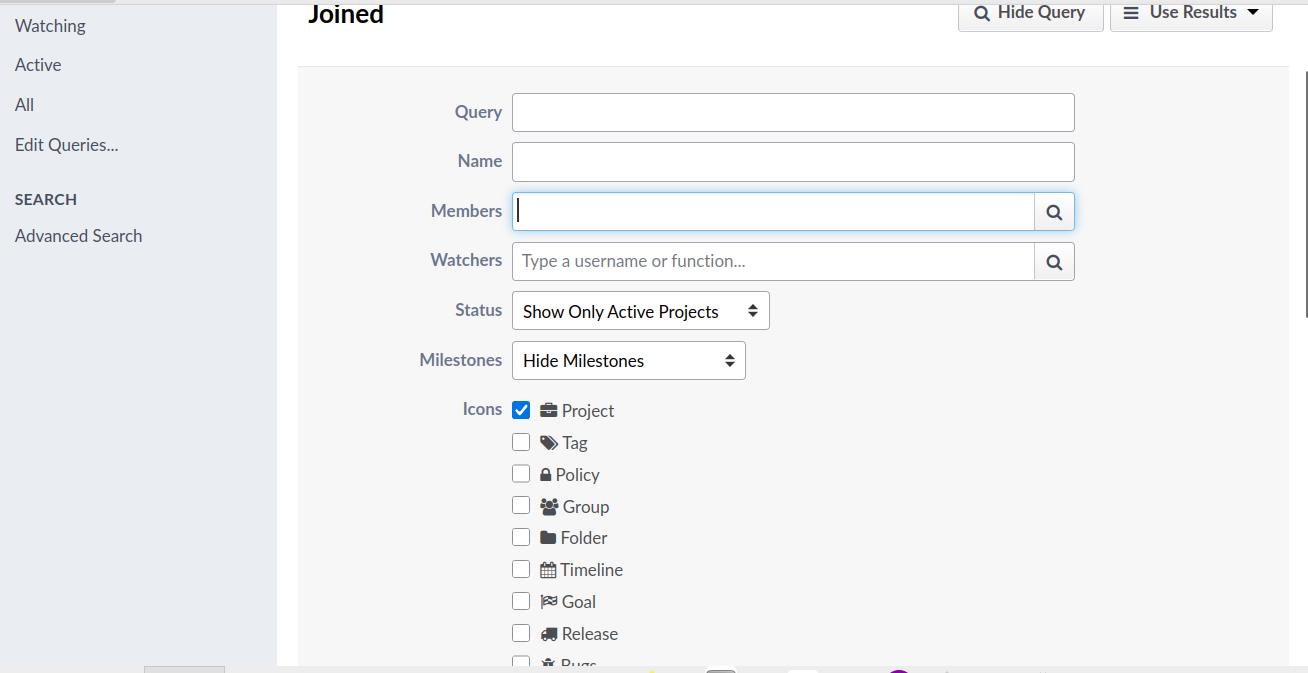 Scroll down and select Project on the “Icons” checklist. 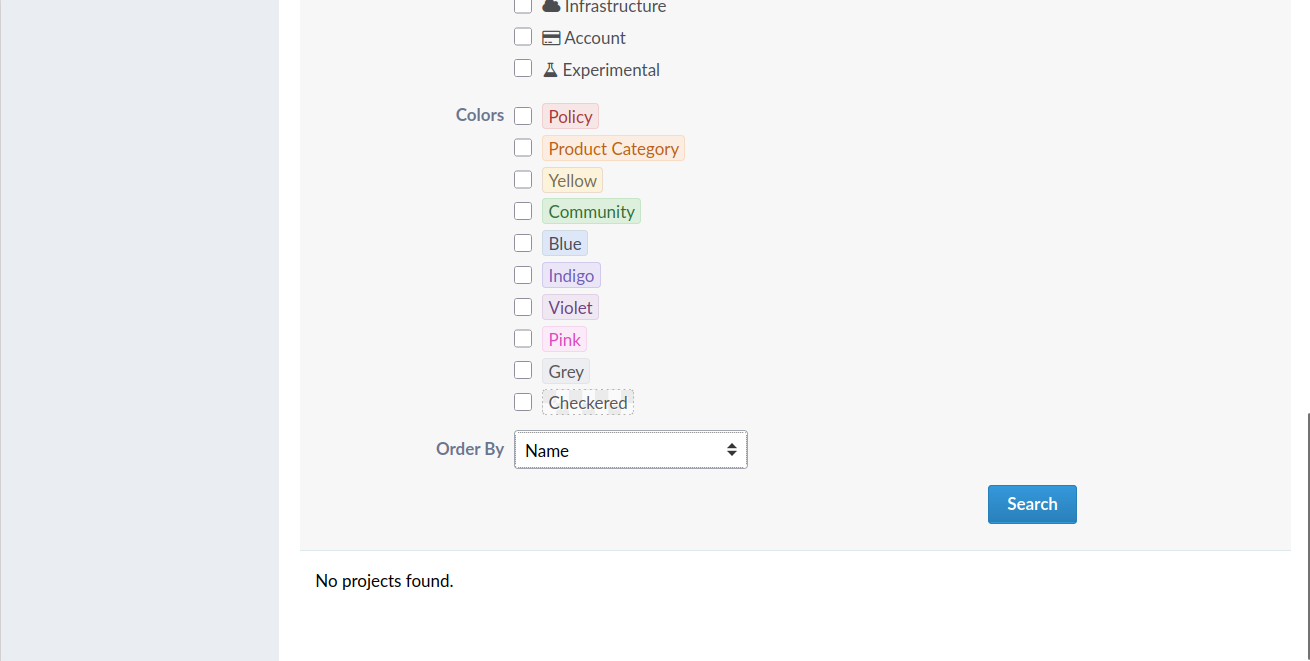 Scroll down and select Search.  Choose a project. 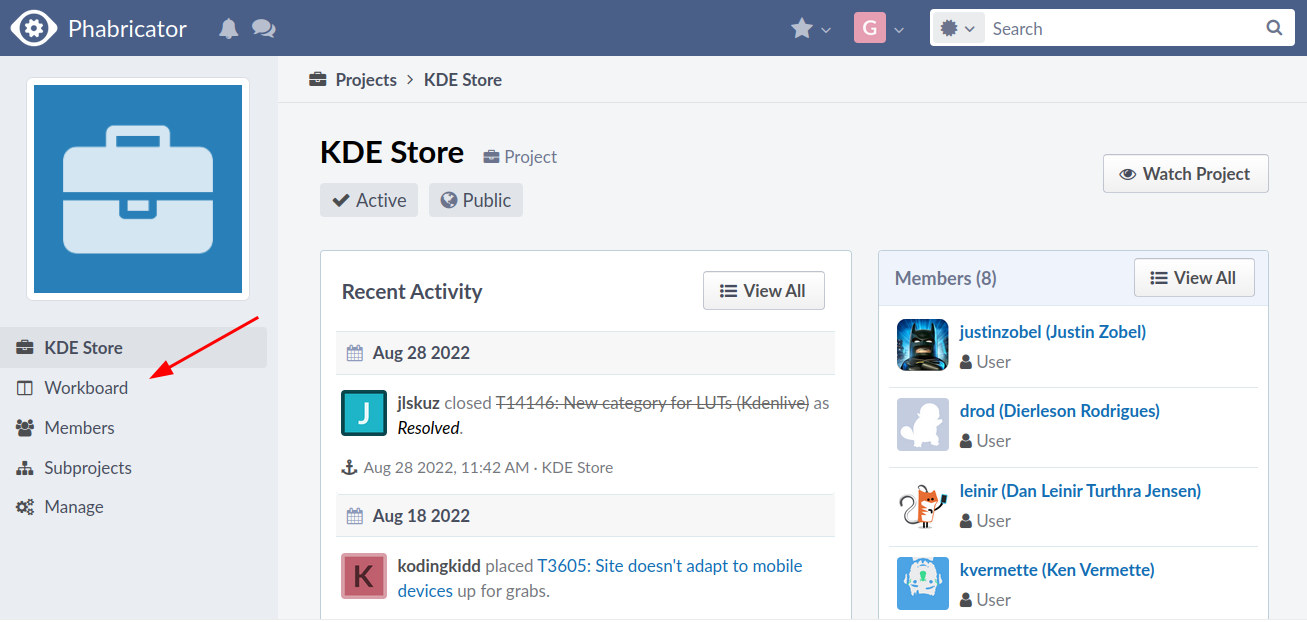 Click on Workboard on the Left sidebar. 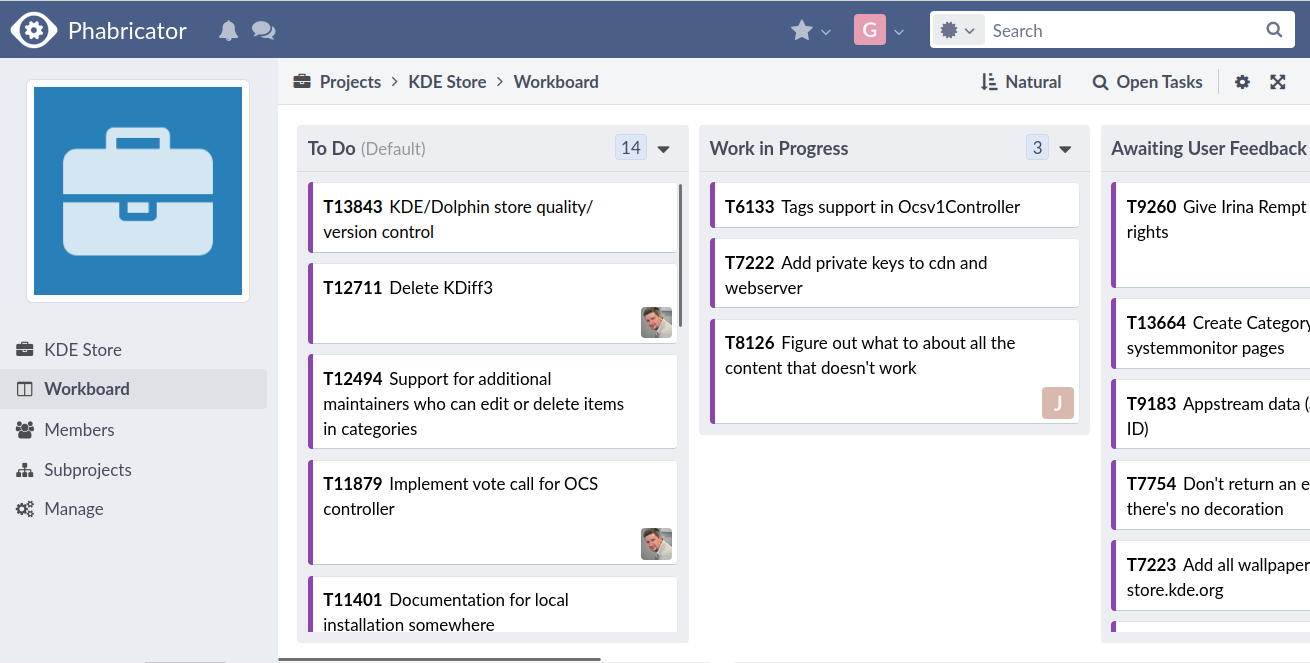 Use the Kanban tool to familiarize yourself with a project’s tasks. Click on a task and join the discussion. BugsGo to https://bugs.kde.org/. 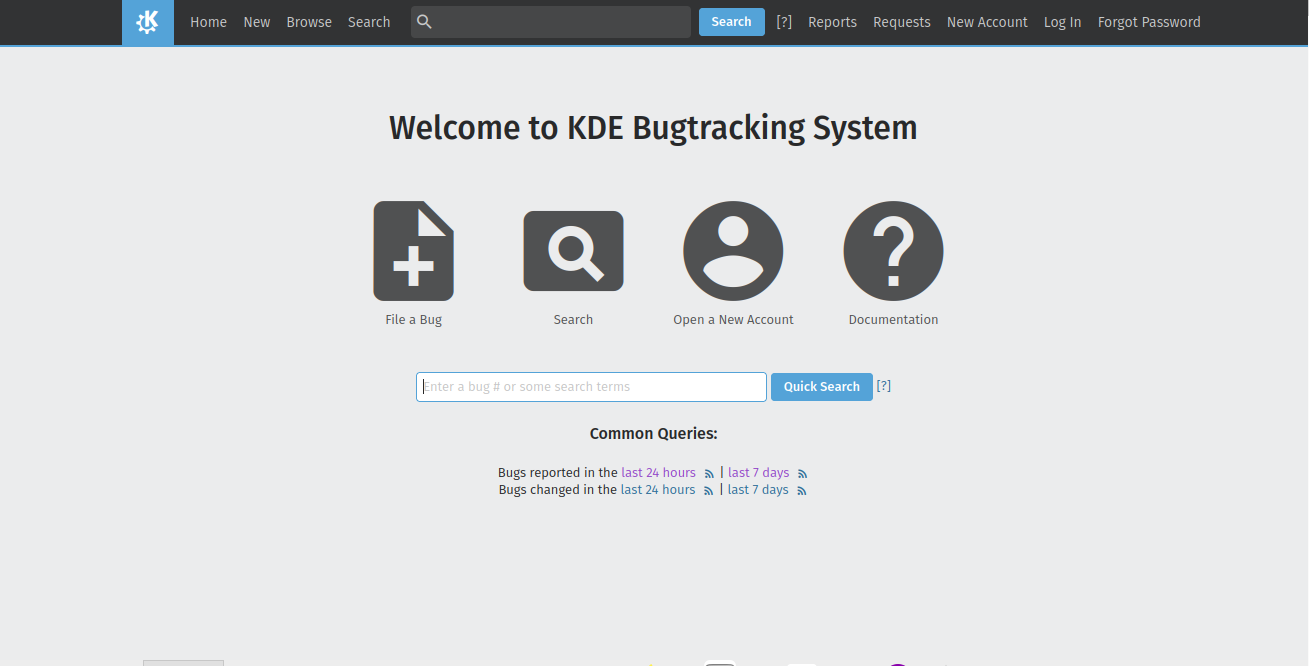 Select the Search icon in the middle of the homepage. 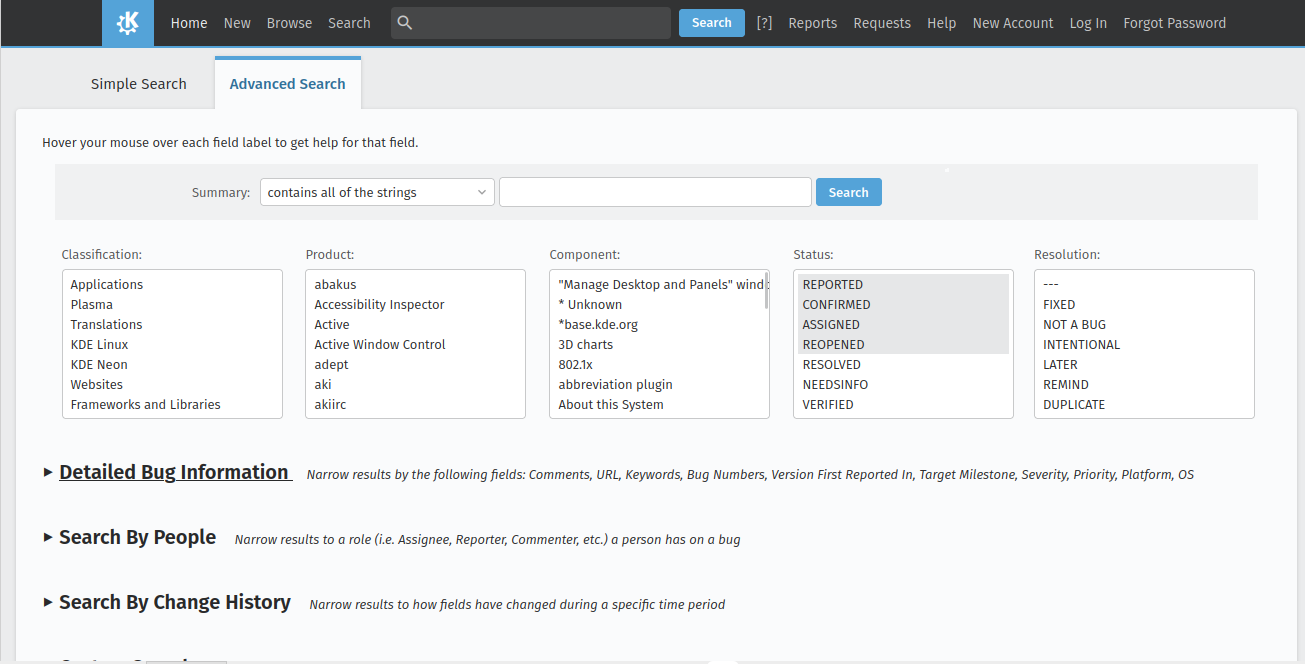 If you’ve never used KDE Bugtracker, choose Advanced Search. 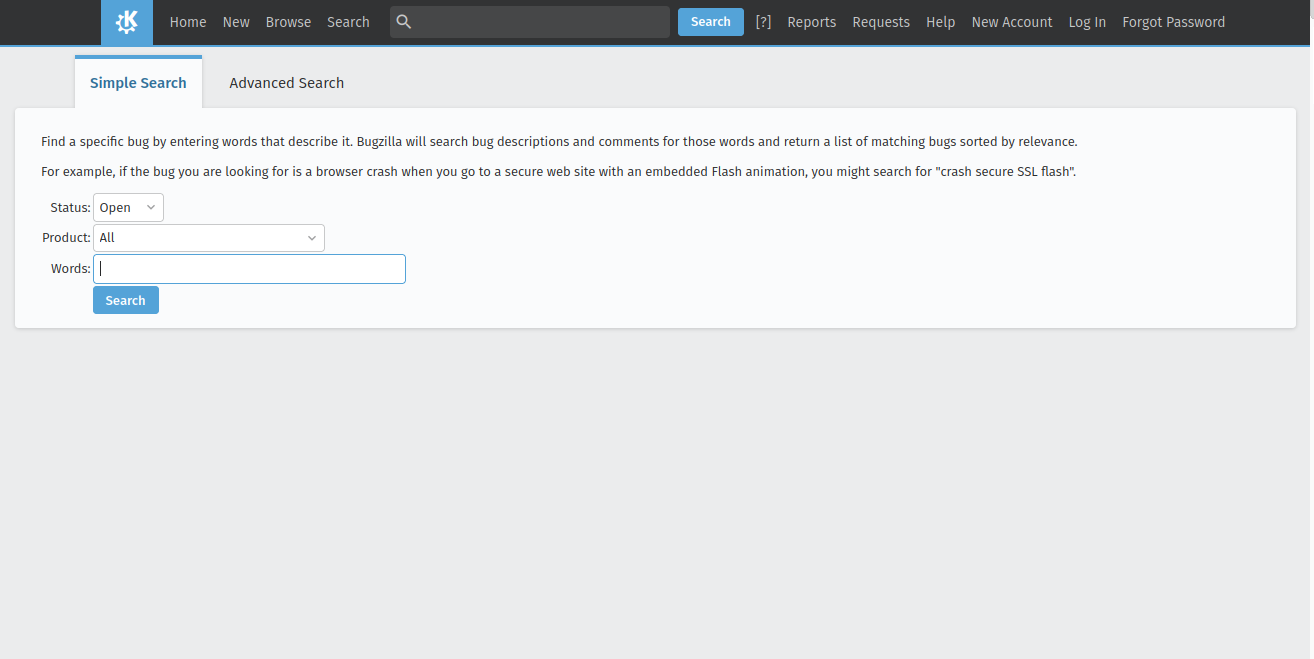 Otherwise, use simple search: select a KDE product, enter keyword(s) and Search.  Use the Classification listbox to select a project you’d like to work on. Note, you can use the Shift or the Ctrl button(s) on your keyboard to select multiple projects within the KDE Bugtracker listboxes. Choose a specific product(s) in the Product listbox. Select Component(s) in the Component listbox. Choose Status for a bug. Select Resolution in the Resolution listbox. Click Search above the listboxes next to the search bar.  Choose a bug from the list of bugs generated by KDE Bugtracker. Patch Bugs with KDE Software Developers. |
To start contributing, you need a KDE Identity account. Work happens on KDE GitLab, KDE Phabricator, and KDE Bugtracker. You can get in touch with KDE developers via
- IRC
- Forum
- GitLab
- Phabricator
- KDE Bugtracker
Contact KDE Software developers |
|---|
| Need assistance? Support is available around the clock. Don’t hesitate to ask questions—everyone starts somewhere.
You can reach the KDE developer community through:
|
