User:Nmariusp/Qt Creator
Qt Creator is an IDE from Qt.
A screen recording version is available https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ASnDeEaXnbI https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QVgInye6HDA
Features
Qt Creator is a good choice when starting to contribute to KDE.
Qt Creator has: support for kdesrc-build, a good debugger, source code navigation, Qt widgets UI designer, basic QML editor, QML debugger, Qt resources editor, Qt project templates, good CMake support, C++ static analyzers.
Additional features:
- Source code navigation: switch header/source, follow symbol, switch between function declaration/definition, find references, open type hierarchy, open include hierarchy.
- Refactor rename symbol.
- Views: class view, tests view, document outline view and document outline combo box, CMake structure view, file system view.
For best results, download Qt Creator from the Qt website. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QVgInye6HDA
kdesrc-build
After you configure kdesrc-build and you can correctly build a KDE project such as kcalc.
Edit ~/.config/kdesrc-buildrc . It should look like:
...
include-dependencies true
...
kdedir ~/kde/usr
...
source-dir ~/kde/src
...
build-dir ~/kde/build
...
cmake-options -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug
...
The line above is important in order to use the debugger from Qt Creator.
Make sure you have the correct number on the line num-cores .
Build kcalc, make sure there are no errors:
kdesrc-build kcalc
Install Qt Creator
Using the Qt online installer - recommended
The newest version of Qt Creator installed from the Qt website will have the latest features and the latest bug fixes.
Video version https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QVgInye6HDA
Go to https://www.qt.io/ on the top right click on the button "Download. Try.". The web browser navigates to "https://www.qt.io/download", in the top right quarter of the page it says "Open source user? Find out how you can use Qt under the (L)GPL and contribute to the Qt project. Download open source". Click on the button "Download open source". The web browser navigates to https://www.qt.io/download-open-source. In the bottom middle of the page it says "Looking for Qt binaries? Find them in the Qt Online Installer. It will steer you to the right download version and help you install tools and add-on components that are available for your open source license. Download the Qt Online Installer". Click on the button "Download the Qt Online Installer" > Linux > "Qt Online Installer for Linux (64-bit)". A file named e.g. qt-unified-linux-x64-4.6.1-online.run is downloaded.
chmod +x qt-unified-linux-x64-4.6.1-online.run ./qt-unified-linux-x64-4.6.1-online.run
The Qt online installer will start. The Qt online installer requires that you create an online user account for https://www.qt.io .
From Linux OS binary packages
E.g.
apt install qtcreator
QML Designer
Qt Creator has a "forms editor" for QML. You can enable it from the Qt Creator main menu > Help > About Plugins... > Qt Quick > enable "QmlDesigner". If it asks you to restart Qt Creator, do it.
Test it. From Qt Designer main menu > File > Close all Files and Editors. File > New Project... > Application (Qt) > Qt Quick Application, finish the wizard correctly. Open the file "Main.qml" in "Switch to Edit mode Ctrl+2". In the left hand side, choose "Switch to Design mode Ctrl+3".
From the Qt Creator main menu > View > Workspaces > Views-All. Close all of the tool windows (views) that you do not need, e.g. "3D", "States", "Timeline", "Curves", "Transitions".
Open a KDE project in Qt Creator >= 15
Please make sure that you use Qt Creator version 15 or newer.
We'll use kcalc as an example KDE Git repository. First, make sure it was built correctly using kdesrc-build.
kdesrc-build kcalc
Start Qt Creator (for example, from the KDE Application Launcher).
From the Qt Creator main menu, select File > "Open File or Project" > ~/kde/build/kcalc/CMakeCache.txt. Click on the button "Configure Project".
Run
cat ~/kde/build/kcalc/prefix.sh
says:
export PATH=/home/username/kde/usr/bin:$PATH
export XDG_DATA_DIRS=/home/username/kde/usr/share:${XDG_DATA_DIRS:-/usr/local/share:/usr/share}
export XDG_CONFIG_DIRS=/home/username/kde/usr/etc/xdg:${XDG_CONFIG_DIRS:-/etc/xdg}
export QT_PLUGIN_PATH=/home/username/kde/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/plugins:$QT_PLUGIN_PATH
export QML2_IMPORT_PATH=/home/username/kde/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/qml:$QML2_IMPORT_PATH
export QT_QUICK_CONTROLS_STYLE_PATH=/home/username/kde/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/qml/QtQuick/Controls.2/:$QT_QUICK_CONTROLS_STYLE_PATH
export MANPATH=/home/username/kde/usr/share/man:${MANPATH:-/usr/local/share/man:/usr/share/man}
export SASL_PATH=/home/username/kde/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/sasl2:${SASL_PATH:-/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/sasl2}
Run:
source ~/kde/build/kcalc/prefix.sh echo PATH=$PATH echo XDG_DATA_DIRS=$XDG_DATA_DIRS echo XDG_CONFIG_DIRS=$XDG_CONFIG_DIRS echo QT_PLUGIN_PATH=$QT_PLUGIN_PATH echo QML2_IMPORT_PATH=$QML2_IMPORT_PATH echo QT_QUICK_CONTROLS_STYLE_PATH=$QT_QUICK_CONTROLS_STYLE_PATH echo MANPATH=$MANPATH echo SASL_PATH=$SASL_PATH
says:
PATH=/home/username/kde/usr/bin:/home/username/.local/bin:/home/username/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/bin:/home/username/.local/share/JetBrains/Toolbox/scripts XDG_DATA_DIRS=/home/username/kde/usr/share:/usr/local/share:/usr/share:/var/lib/snapd/desktop XDG_CONFIG_DIRS=/home/username/kde/usr/etc/xdg:/home/username/.config/kdedefaults:/etc/xdg QT_PLUGIN_PATH=/home/username/kde/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/plugins: QML2_IMPORT_PATH=/home/username/kde/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/qml: QT_QUICK_CONTROLS_STYLE_PATH=/home/username/kde/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/qml/QtQuick/Controls.2/: MANPATH=/home/username/kde/usr/share/man:/usr/local/share/man:/usr/share/man SASL_PATH=/home/username/kde/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/sasl2:/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/sasl2
Save the text block above to file ~/kde/expanded-prefix-sh.txt. The same text block will be needed when opening in the IDE Qt Creator other KDE project. The content of this file is also needed when running or debugging a KDE project in other IDEs e.g. JetBrains CLion.
Build the project
You can build by pressing the hammer icon on the lower left with tooltip "Build Project Ctrl+B", Or from the Qt Creator main menu > Build > Build Project "kcalc".
Try the debugger
In the left sidebar, switch to Edit mode (Ctrl+2). Select "Projects" from the drop-down menu at the top of the leftmost panel. Expand kcalc > kcalc > Source Files > double click on the file kcalc.cpp to show it in the editor view.
In the text editor's top bar, open the <Select Symbol> drop-down menu, scroll to the bottom of the options, and select the last item in it: main(int, char**) -> int. Click on the line with the opening curly bracket of the function main. Set a breakpoint by opening the Debug menu > Set or Remove Breakpoint (F9).
Start debugging the project by opening the Debug menu > Start Debugging > Start Debugging of Startup Project (F5). The debugger will start and pause execution on the source code line with the curly bracket.
Use the debugger by opening the Debug menu > Step Over (F10)/Step Into (F11)/Step Out (Shift+F11).
Enable parallel jobs in Qt Creator
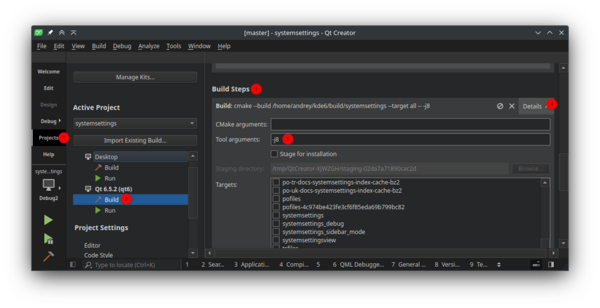
- Left Sidebar > Switch to Projects mode (Ctrl+5).
- Under the Build settings of the imported kit find the "Build Steps" option.
- Click on the "Details" button on the right side of the "Build Steps" option to access the detailed build configuration.
- Under the "Tool arguments" field add the argument
-j<jobs>. Replace "<jobs>" with the desired number of parallel jobs you want to use during compilation. For example, if you have a CPU with 16 threads and want to use 12 parallel jobs, you would enter-j12.
- Rebuild your project to get faster compilation.
Tips and Tricks
Custom executable to run
When developing a library, it may be convenient to launch some application that uses it, from the current project. For example, you work with Ark's libraries used in dolphin context menu actions. You can make your run configuration to launch custom binary - dolphin. See documentation on how to configure that.